ADMIN
The Empire


الرتبة : ادارة الموقع
عدد المساهمات : 1203
Level : 2104
Like : 5
تاريخ الميلاد : 29/05/1988
تاريخ التسجيل : 20/12/2010
العمر : 35
 المزاج : مزاج طبيب أسنان ممارس المزاج : مزاج طبيب أسنان ممارس
 |  موضوع: Oral Submucous Fibrosis موضوع: Oral Submucous Fibrosis  26/02/12, 11:29 pm 26/02/12, 11:29 pm | |
| Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Definition of Oral Precancerous Condition: A generalised pathological state of the oral mucosa associated with a significantly increased risk of cancer.
Oral Submucous Fibrosis: a chronic debilitating disease of
the*oral cavity*characterized by inflammation and
progressive*fibrosis*of the*sub mucosal tissues.
Clinical Features:
Early OSF-Prodromal symptoms: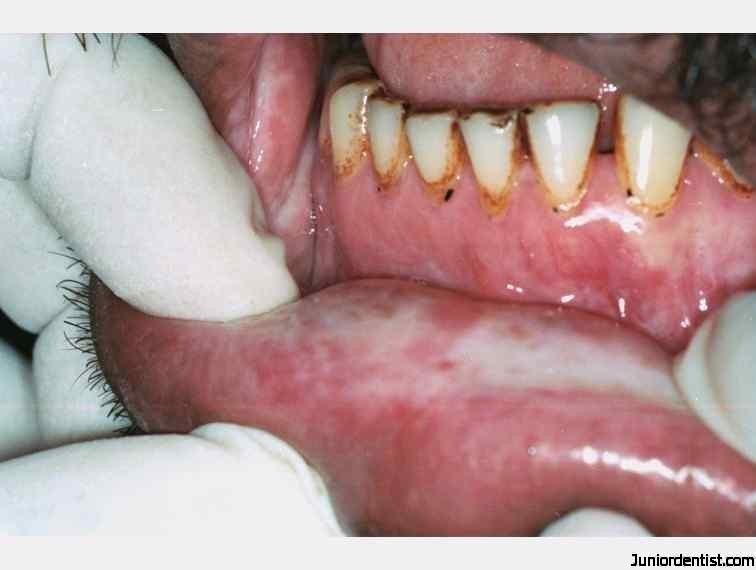
Burning sensation in the mouth on consuming spicy food,
Blisters on the palate
Ulcerations or recurrent generalized inflammation of the oral mucosa,
excessive salivation,
defective gustatory sensation,
dryness of the mouth
Periods of exacerbations with appearance of small vesicles in the cheek and palate.
Petichiae are observed on tongue followed by labial and buccal mucosa.
Pain in area with submucosal fibrotic bands on palpation is a useful clinical test.
Histologically-
Hyperplastic epithelium
Numerous dilated and blood filled capillaries juxtaepithelially.
Inflammatory cells: lymphocytes, plasma cells.
Large number of Lymphocytes, fibroblasts and plasma cells suggest *tissue reaction leading to* OSF
Advanced OSF: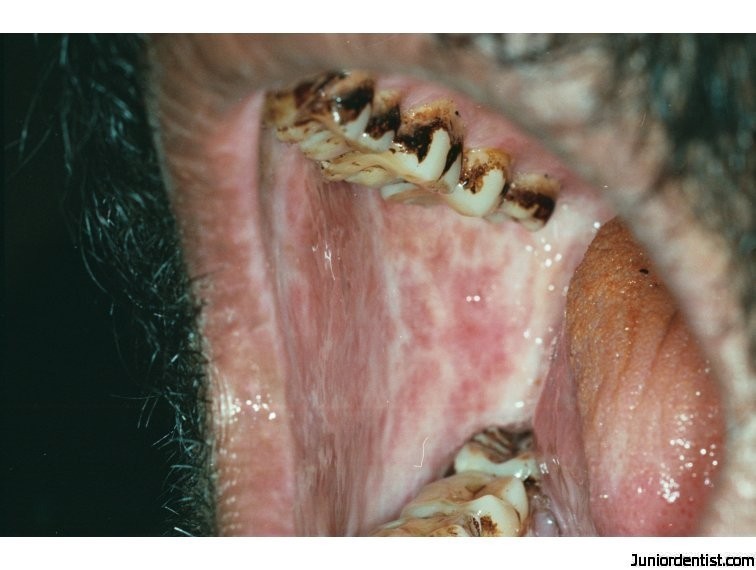
Oral mucosa* becomes blanched and slightly opaque and white fibrous bands appear
Buccal mucosa, lips, palate and faucial pillars are affected
Oral mucosa is involved symmetrically and fibrous bands in the buccal mucosa run in vertical direction
Soft Palate:
initially: fibrous depostis varies from slight whitish areas on soft palate, with no symptoms
later: dense fibrosis, causing fixation and shortening or even deviation of uvula and soft palate.
Faucial Pillars: ranges from slight sub mucosal accumulation in both
pillars to a dense fibrosis extending deep into the pillars with
strangulation of tonsils.
Difficulty in mouth opening is due to Dense Fibrosis involving the tissues around the pterygomandibular raphae.
In severe cases the Fibrosis may spread to Pharynx and down the piriform fossae
Circular bands are felt around the entire Rima Oris(mouth orifice) and seen more around the lower lip.
Tongue: Decreased movement and atrophy of tongue papillae.
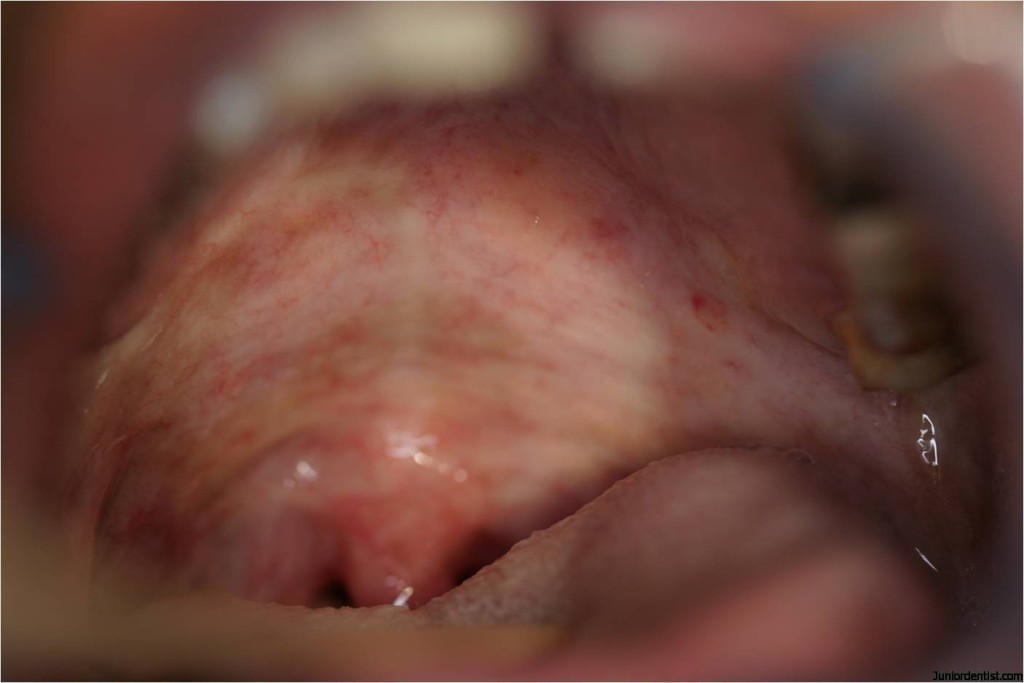
With Progressive fibrosis the following changes can be seen :
- Difficulty in mouth opening
- Inability to whistle
- Difficulty to blow out a candle
- Difficulty in swallowing
Fibrosis involving Nasopharynx:* Referred pain to the ear, nasal voice
Epidimiology:
Sex- F>M
Etiology:
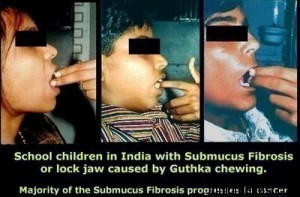
- Habitual areca Nut chewing is the main cause which leads to
- Stimulation of Fibroblast proliferation leading to excessive collagen synthesis.
- Decreased secretion of collagenase
Pathology:
Structural and Microstructural changes:
Epithelial changes in different* stages of OSF
Early stage – Hyperplasia
Advanced stage – Atrophy
Lesions of Palate – Orthokeratosis
Lesions of the buccal mucosa – Parakeratosis
Sub Epithelial changes:
On the basis of histopathological appearances OSF can be divided into 4 stages:
- Very early
- Early
- Moderately advanced
- Advanced
Criteria for classification:
- Subepithelial collagen
- Presence or absence of edema
- Physical state of mucosal collagen
- State of blood vessels
Predominant inflammatory cell types are mainly lymphocytes and plasma cells
Management:
The reduction or even elimination of the habit of arecanut chewing is an important preventive measure.
Nutritional Support
Immunomodulatory drugs
Physiotherapy
Local Drug delivery – Local injections of Corticosteroids and Placental Extracts
Combined Therapy – All the above techniques are used together
Surgical Management- Forcing the mouth open and cutting the fibrotic bands
| |
|

